Quality evaluation of livestock and poultry manure in black soil area of Songnen Plain
-
摘要:
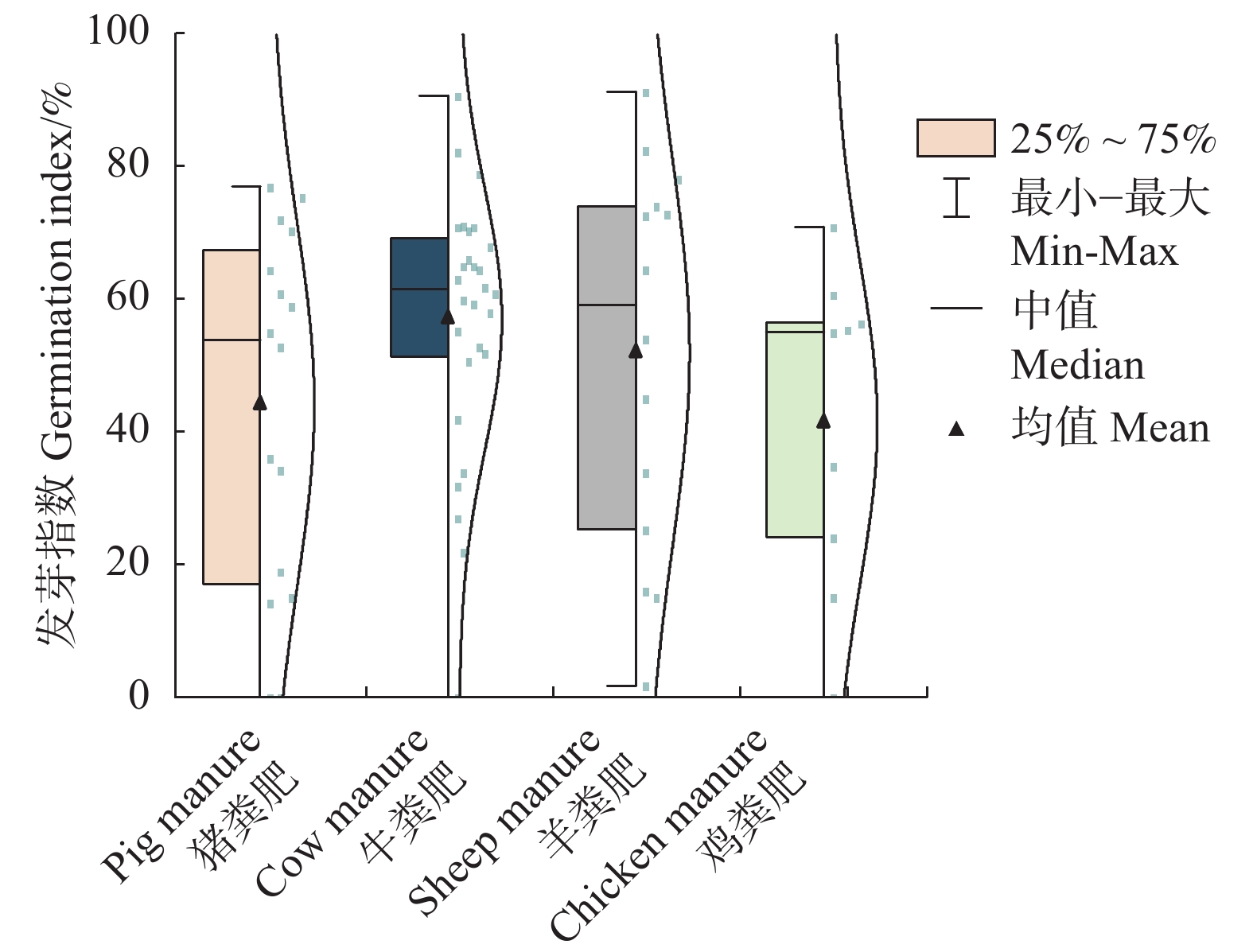
明确松嫩平原黑土区畜禽粪肥品质差异,可为其质量提升及合理施用提供理论依据。本研究于黑龙江省松嫩平原黑土区采集猪粪、牛粪、羊粪和鸡粪4种堆肥样品67个,通过测定不同种类畜禽粪肥技术指标、限量指标及有机组分含量,建立畜禽粪肥质量综合得分模型,从而对其质量进行评价。结果表明:(1)猪粪肥、牛粪肥、羊粪肥和鸡粪肥的平均种子发芽指数(GI)分别为44.1%、57.0%、51.9%和41.4%,均接近或大于50%的畜禽粪肥无害化要求,但小于有机肥NY/T525-2021标准70%的要求;(2)4种畜禽粪肥中,牛粪肥各项指标都更接近于NY/T525-2021标准要求,且牛粪肥中较活跃的有机组分可溶性有机质(DOM)、可提取腐殖酸(HE)、胡敏酸(HA)、富里酸(FA)含量均高于其他3种;(3)在畜禽粪肥质量评价综合得分模型中,牛粪肥获得最高得分0.834,其它粪肥得分依次为:羊粪肥0.761、猪粪肥0.732、鸡粪肥0.508。总体来看,4种畜禽粪肥的腐熟度仍需进一步提高,其综合质量排序为:牛粪肥 > 羊粪肥 > 猪粪肥 > 鸡粪肥。
Abstract:Clarifying the quality differences of livestock and poultry manure in black soil area of Songnen Plain, Heilongjiang Province, can provide theoretical basis for its quality improvement and rational application. In this study, 67 compost samples of pig manure, cattle manure, sheep manure and chicken manure were collected from the black soil area of Songnen Plain, Heilongjiang Province. By measuring the technical indexes, limit indexes and organic components of different livestock manure, a comprehensive score model was established to evaluate the quality of livestock manure. The results show that: (1) The average seed germination index (GI) of pig manure, cattle manure, sheep manure and chicken manure are 44.1%, 57.0%, 51.9% and 41.4%, respectively, which is close to or greater than 50% of livestock manure harmless requirements, but lower than 70% of organic manure NY/T525-2021 standard requirements; (2) Among the four kinds of livestock and poultry manure, all indexes of cattle manure are closer to the requirements of NY/T525-2021 standard, and the contents of soluble organic matter (DOM), extractable humic acid (HE), humic acid (HA) and fulvic acid (FA) in cattle manure are higher than those of the other three kinds; (3) In the comprehensive score model of livestock and poultry manure quality evaluation, cattle manure is with the highest score of 0.834, and the scores of other manures are 0.761 sheep manure, 0.732 pig manure and 0.508 chicken manure. Overall, the maturity of the four kinds of livestock and poultry manure still needs to be further improved, and its comprehensive quality is in the order of cattle manure > sheep manure > pig manure > chicken manure.
-
0 引 言
东北黑土区是我国重要的粮食产区和商品粮基地,在保障国家粮食安全中发挥着举足轻重的作用,已成为我国粮食生产的“压舱石”[1]。然而,自20世纪50年代大规模开垦以来,黑土地经长期高强度利用,加之风蚀、水蚀及融蚀等不利因素的影响,黑土层逐年变薄,土壤表层有机质含量显著下降,土壤理化性状与生态功能严重退化[2]。施用有机肥是改善黑土肥力退化现状、提升黑土可持续生产力的重要措施[3]。畜禽粪肥作为有机肥最重要的来源,在东北黑土区产量大,年产约为4.7亿t,其中猪、牛、羊、鸡粪是畜禽粪便最主要的资源,占比可达90%以上[4]。东北黑土区农户多将猪、牛、羊、鸡粪自然堆置后施入土壤,由于堆置过程以及物料来源本身的差异,导致其施用后对作物产量、土壤理化性状的影响变异性较大[5]。因此,明确黑土区猪、牛、羊、鸡粪肥品质差异,对于其质量提升及合理施用具有重要意义。
目前国内对于有机肥质量评价主要集中在种子发芽指数(GI)、有机质和总养分含量等有机肥技术指标和重金属含量等限量指标上,对有机肥中的有机组分关注较少。而有机肥中可溶性有机质(DOM)、可提取腐殖酸(HE)、胡敏酸(HA)、富里酸(FA)等有机组分在改善土壤质量、促进作物生长等方面有着更为突出作用[6 − 7]。因此,本研究基于NY/T525-2021中有机肥料质量评价指标,结合有机质组分差异,通过主成分分析法建立畜禽粪肥质量综合评价体系,分析了黑龙江省松嫩平原黑土区主要典型区域的猪粪、牛粪、羊粪、鸡粪4种堆肥样品品质差异,旨在为黑土区畜禽粪肥的品质提升提供数据支撑。
1 材料与方法
1.1 样品采集
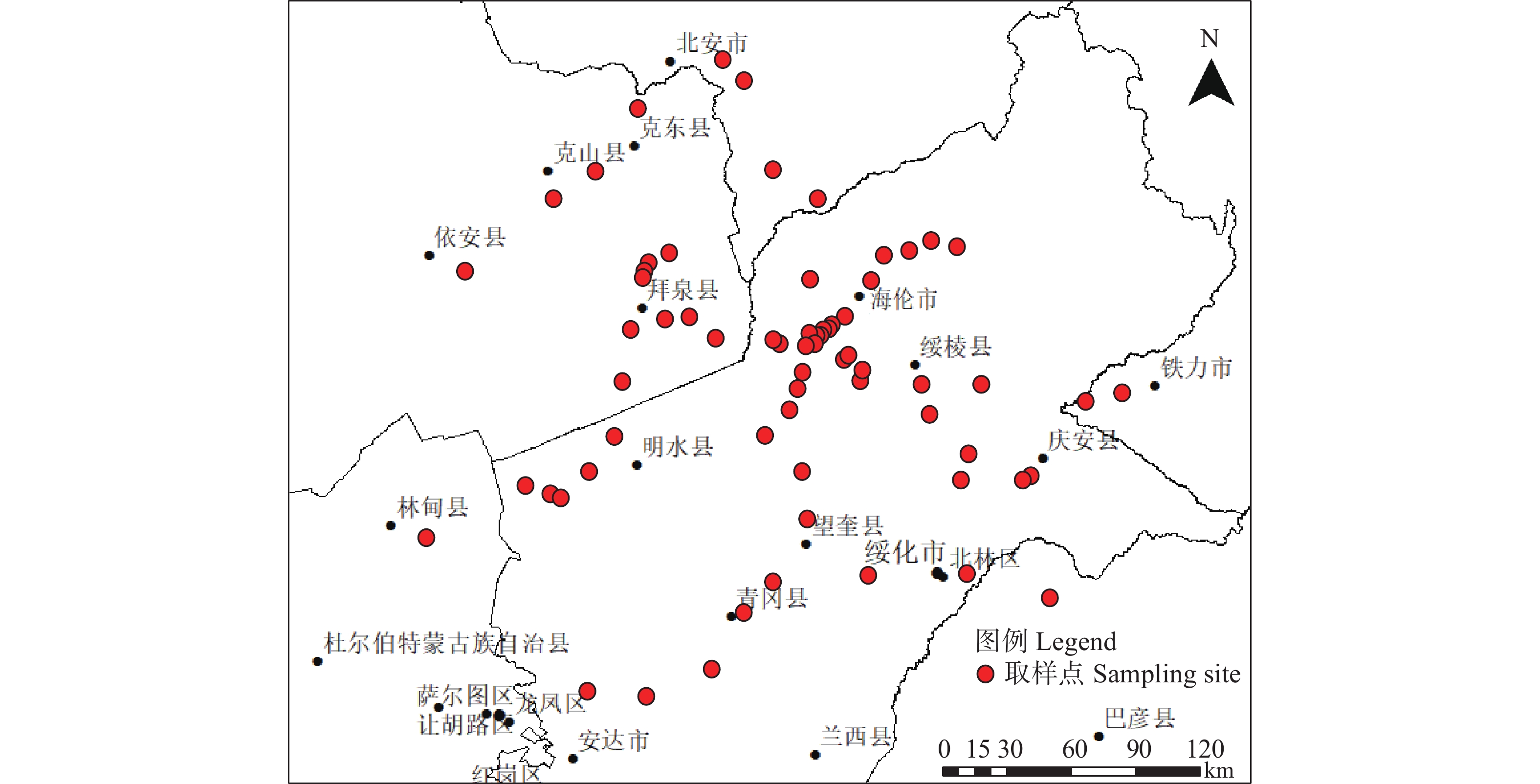
于黑龙江省松嫩平原黑土区齐齐哈尔、黑河、大庆、绥化、伊春、哈尔滨等地采集猪、牛、羊、鸡粪4种堆肥样品共67个,采样点见图1。其中猪粪肥样品16个,牛粪肥样品28个,羊粪肥样品14个,鸡粪肥样品9个。
采样方法:将堆体竖切,于堆体上中下随机采集样品,混匀,用四分法将样品缩分至2.2 kg。其中600 g鲜样用于水分和种子发芽指数测定,1 000 g鲜样用于杂草种子活性测定,500 g样品风干后用于机械杂质测定,最后100 g样品风干研磨后过20目筛用于成分分析。
1.2 样品测定
(1)有机肥限量指标及技术指标测定:参考有机肥农业行业标准(NY/T525-2021)[8]。
(2)有机质化学分测定[9]:取过60目筛风干样品2.0 g于50 mL离心管中,加30 mL蒸馏水,用涡旋仪混匀,于水浴恒温振荡器(70 ℃,180 r·min−1)浸提1 h,取下冷却后以4 000 r·min−1离心10 min,上清液过滤至50 mL容量瓶中,再加20 mL蒸馏水于离心管,涡旋混匀后离心,上清液合并,用蒸馏水定容,此溶液为可溶性物质。于离心管沉淀中加入30 mL焦磷酸钠与氢氧化钠混合液(0.1 mol·L−1 NaOH+0.1 mol·L−1 Na4P2O7,V/V=1∶1)涡旋混匀后于水浴恒温振荡器(70 ℃,180 r·min−1)浸提1 h,取下冷却后以4 000 r·min−1离心10 min,上清液过滤至50 mL容量瓶中,再加20 mL混合液清洗残渣两次(每次10 mL),将2次清洗的离心液合并过滤于上述50 mL容量瓶中,此溶液为可提取腐殖酸。离心管中沉淀用20 mL蒸馏水清洗离心两次,弃去上清液,于55 ℃烘干,过60目筛,即为胡敏素。取可提取腐殖酸溶液20 mL至50 mL离心管,滴加0.5 mol·L−1H2SO4调节pH至1.0 ~ 1.5,将此溶液于70 ℃下保温1.5 h,取下后室温下静置10 h,将溶液过滤定容于50 mL容量瓶中,此溶液为富里酸。滤纸上的沉淀用0.25 mol·L−1H2SO4洗涤3次,弃去洗涤液,用≥60 ℃的0.05 mol·L−1 NaOH溶液,将滤纸上的沉淀溶解,后将溶解液转移至50 mL容量瓶中,用蒸馏水定容,此溶液为胡敏酸。
通过K2Cr2O7 容量法测定可溶性物质、可提取腐殖酸、胡敏酸溶液及胡敏素碳量可得各组分的含量,富里酸含量=可提取腐殖酸含量-胡敏酸含量[10]。
1.3 数据处理
试验数据整理和计算采用Microsoft Excel 2016完成,采用SPSS27进行数据分析及主成分分析,采用 Origin2021和PowerPoint 2016进行绘图。
2 结果与讨论
2.1 不同畜禽粪肥技术指标差异
技术指标注重有机肥的营养成分、肥力肥效和作物保护等方面要求。种子发芽指数(GI)是评价畜禽粪肥腐熟度最可靠的指标,反映堆肥是否无毒无害、安全可用。NY/T525-2021[8]要求GI需达到70%,即堆肥完全腐熟;也有研究认为GI达到50%,即可认为堆肥对作物种子基本无毒性[11 − 13]。本研究测定结果表明,各畜禽粪肥平均GI范围在41.4% ~ 57.0%,多数满足畜禽粪肥无害化50%的要求,但未达到70%。而牛粪肥和羊粪肥平均GI都超过50%,已达到对种子基本无毒的水平,牛粪肥平均GI更是达到57%(图2),说明在实际应用中,施用牛粪肥相较于其他3种粪肥更加安全。
有机质的质量分数、总养分的质量分数是代表有机肥肥力的指标。NY/T525-2021[8]要求有机质的质量分数≥30%,是对其作为有机肥的基本要求。然而,有机质的质量分数会随着堆肥腐熟度提高而降低[14],因此过高的有机质含量,可能伴随低腐熟度的风险,如表1中猪粪肥的平均有机质含量要高于牛粪肥,但其平均GI比牛粪肥低13%。总养分的质量分数则表示有机肥中氮、磷、钾养分的含量,4种畜禽粪肥养分含量变异较大,主要是由于堆肥中养分含量会随腐熟度变化而变化,且堆置环境和堆置方法的差异也会对堆肥养分含量造成影响[15]。
表 1 不同畜禽粪肥的技术指标Table 1 Technical indexes of different livestock and poultry manure技术指标
Technical index猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manure有机质的质量分数
Organic matter content范围Range/% 21.5 ~ 86.5 24.1 ~ 82.1 31.4 ~ 78.2 27.9 ~ 60.4 中值Median/% 46.9 44.6 45.6 39.9 均值Mean/% 48.5 45.4 48.1 40.4 变异系数Coefficient 42.3 32.0 25.0 23.9 标准Criteria/% ≥30 ≥30 ≥30 ≥30 达标率Compliance rate/% 81 89 100 89 总养分的质量分数
Total nutrient content范围Range/% 3.14 ~ 8.86 2.65 ~ 7.97 2.84 ~ 5.71 2.25 ~ 4.87 中值Median/% 5.00 4.06 4.26 3.87 均值Mean/% 5.39 4.29 4.39 3.83 变异系数Coefficient 35.2 29.7 18.8 21.1 标准Criteria/% ≥4 ≥4 ≥4 ≥4 达标率Compliance rate/% 75 57 71 44 酸碱度
pH范围Range 5.9 ~ 8.7 6.4 ~ 8.6 6.0 ~ 9.4 7.0 ~ 9.0 中值Median 7.8 7.8 8.1 8.3 均值Mean 7.5 7.7 8.0 8.0 变异系数Coefficient 13.1 6.7 12.3 8.1 标准Criteria 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 96 71 78 水分的质量分数
Moisture content范围Range/% 15.7 ~ 68.0 15.0 ~ 59.0 17.8 ~ 60.6 17.5 ~ 37.0 中值Median/% 43.0 28.2 29.5 28.0 均值Mean/% 39.5 31.7 33.6 28.4 变异系数Coefficient 38.9 42.0 39.4 19.7 标准Criteria/% ≤30 ≤30 ≤30 ≤30 达标率Compliance rate/% 38 64 50 67 机械杂质质量分数
Mechanical impurity content范围Range/% 0 ~ 0.99 0 ~ 0.97 0 ~ 0.96 0.52 ~ 0.97 中值Median/% 0.61 0.43 0.41 0.86 均值Mean/% 0.53 0.42 0.44 0.80 变异系数Coefficient 67.4 85.7 87.0 43.3 标准Criteria/% ≤0.5 ≤0.5 ≤0.5 ≤0.5 达标率Compliance rate/% 38 57 57 0 注:各指标标准参考有机肥农业行业标准(NY/T525-2021)[8]。 Note: The index standards refer to the Agricultural Industry Standard of Organic Fertilizer (NY/T525-2021)[8]. 牛粪肥、鸡粪肥的总养分质量分数达标率相比猪粪肥和羊粪肥略低,但是牛粪肥平均总养分质量分数达到4.29%,已超过标准中要求的4%,且牛粪肥的氮、磷、钾养分比例为2∶1∶1.5,更接近于多数作物需求的养分比例。鸡粪肥平均总养分质量分数仅为3.83%。4种畜禽粪肥酸碱度均偏碱性,超标的部分集中在pH > 8.5的部分,生产利用中需根据土壤酸碱度进行调整。
水分质量分数会影响有机肥的运输及施用。4种畜禽粪肥中,猪粪肥的达标率仅38%,这可能是由于猪圈、猪场未进行粪尿分离,制作猪粪堆肥的水分含量整体偏高所致。机械杂质的质量分数主要影响肥料的商品属性,鸡粪肥的机械杂质含量极高,所有鸡粪肥样品机械杂质含量均超标。
2.2 不同畜禽粪肥限量指标差异
有机肥限量指标聚焦在有机肥施用导致的土壤污染、环境破坏等方面的问题[16 − 17],对有机肥中重金属、盐分含量及杂草种子活性做出规定要求。4种畜禽粪肥的限量指标测定结果(表2),猪粪肥、牛粪肥、羊粪肥的各项重金属含量达标率均超过80%,而鸡粪肥的砷(As)、镉(Cd)、铅(Pb)含量达标率低于80%,尤其是Pb含量,达标率仅33%。4种畜禽粪肥的铬(Cr)、汞(Hg)含量达标率均为100%,因此,在使用畜禽粪肥时需重点关注肥料中As、Cd、Pb含量是否达标,避免造成土壤重金属污染。
表 2 不同畜禽粪肥的限量指标Table 2 Limit indexes of different livestock and poultry manure限量指标
Limit index猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manureAs 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.95 ~ 15.1 1.55 ~ 19.7 1.68 ~ 20.0 7.59 ~ 16.8 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 4.45 6.50 7.43 9.53 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 5.96 7.71 8.08 12.1 变异系数Coefficient 81.6 69.5 67.0 33.1 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤15 ≤15 ≤15 ≤15 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 86 86 56 Cd 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.74 ~ 3.45 0.28 ~ 2.16 0.28 ~ 3.07 1.07 ~ 3.22 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 1.51 1.34 1.24 1.91 均值Mean(/mg·kg−1) 1.68 1.24 1.44 2.04 变异系数Coefficient 48.9 44.0 52.1 34.4 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤3 ≤3 ≤3 ≤3 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 100 93 78 Cr 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 3.2 ~ 61.4 0.3 ~ 47.9 5.6 ~ 31.0 7.2 ~ 69.1 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 17.1 12.5 11.9 21.8 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 20.0 17.5 15.4 28.0 变异系数Coefficient 70.5 69.1 53.9 84.5 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤150 ≤150 ≤150 ≤150 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 100 Hg 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.08 ~ 0.31 0.05 ~ 0.34 0.04 ~ 0.41 0.07 ~ 1.71 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 0.16 0.12 0.13 0.16 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 0.17 0.13 0.17 0.48 变异系数Coefficient 34.5 52.4 70.4 141.7 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤2 ≤2 ≤2 ≤2 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 100 Pb 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.66 ~ 34.2 1.51 ~ 29.7 1.03 ~ 39.6 33.5 ~ 56.3 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 6.70 10.23 8.53 51.41 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 9.71 11.85 14.0 47.9 变异系数Coefficient 107.1 69.6 98.0 17.8 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤50 ≤50 ≤50 ≤50 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 33 氯离子质量分数
Chloride ion content范围Range/% 0.31 ~ 1.99 0.16 ~ 1.99 0.21 ~ 1.91 1.23 ~ 1.96 中值Median/% 1.15 0.70 1.00 1.69 均值Mean/% 1.20 0.87 1.10 1.60 变异系数Coefficient 47.3 66.5 39.1 18.9 杂草种子活性
Weed seed activity范围Range/(株·kg−1) 0 0 ~ 2 0 ~ 5 0 中值Median/(株·kg−1) 0 1 2 0 均值Mean/(株·kg−1) 0 0.71 2.07 0 变异系数Coefficient 0.0 92.2 83.5 0.0 注:各指标标准参考有机肥农业行业标准(NY/T525-2021)[8]。 Note: The index standards refer to the Agricultural Industry Standard of Organic Fertilizer (NY/T525-2021) [8]. 氯离子质量分数体现有机肥中盐分的含量。猪、羊、鸡粪肥的平均氯离子质量分数偏高,其中鸡粪肥平均氯离子质量分数达到1.6%,对于一些忌氯作物使用时要慎重考虑。杂草种子活性指有机肥中杂草种子的数量及利于杂草生长的因子,猪粪肥和鸡粪肥中均无杂草生长,而羊粪肥中杂草种子活性较高,最高可达5株·kg−1,用时需要注意及时清理杂草。
2.3 不同畜禽粪肥有机组分差异
可溶性有机质(DOM)是有机肥中最活跃、最有效的组分,可直接被微生物和植物吸收利用,其对作物生长具有显著的促进作用[18]。4种畜禽粪肥的平均DOM含量为牛粪肥 > 羊粪肥 > 鸡粪肥 > 猪粪肥(表3)。腐殖酸是指腐殖酸中可溶于碱的一类高分子化合物,是腐殖酸中被作物吸收利用的主要部分[19],4种畜禽粪肥的平均腐殖酸含量为牛粪肥 > 羊粪肥 > 猪粪肥 > 鸡粪肥。胡敏酸是可提取腐殖酸中分子量较大,稳定性较高的组分,是最好的土壤改良剂[20]。4种畜禽粪肥的平均胡敏酸含量为牛粪肥 > 羊粪肥 > 猪粪肥 > 鸡粪肥。富里酸是可提取腐殖酸中分子量较小、活性较大、氧化程度较高的组分[21],4种畜禽粪肥的平均富里酸含量为牛粪肥 > 羊粪肥 > 猪粪肥 > 鸡粪肥。胡敏素是与矿物质紧密结合的腐殖物质,其具有大分子结构,且稳定性较高,对保持土壤结构具有重要的意义[22],4种畜禽粪肥的平均胡敏素含量为猪粪肥 > 牛粪肥 > 鸡粪肥 > 羊粪肥。
表 3 不同畜禽粪肥的有机组分Table 3 Organic components of different livestock and poultry manure有机组分
Organic component猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manure可溶性有机质
Dissolved organic matter范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 1.1 ~ 24.9 5.9 ~ 24.8 5.4 ~ 22.2 4.3 ~ 24.2 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 11.7 14.3 14.0 12.5 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 11.8 14.3 13.8 13.1 变异系数Coefficient 62.0 34.4 37.0 48.2 腐殖酸
Extractable humic acid
范围Range /(g·kg−1) 25.4 ~ 97.4 21.1 ~ 97.4 36.1 ~ 72.6 31.6 ~ 67.5 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 61.1 65.4 60.3 61.4 均值Mean/ (g·kg−1) 56.9 64.8 59.2 55.3 变异系数Coefficient 36.0 29.4 17.7 22.4 胡敏酸
Humic acid
范围Range /(g·kg−1) 8.7 ~ 40.3 6.7 ~ 46.0 7.4 ~ 45.4 14.0 ~ 39.3 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 22.8 27.5 23.5 29.0 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 23.9 27.5 25.1 27.3 变异系数Coefficient 44.1 34.3 46.1 29.0 富里酸
Fulvic acid范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 11.4 ~ 60.4 11.0 ~ 52.5 12.7 ~ 40.0 17.5 ~ 42.3 中值Median /(g·kg−1) 31.3 35.3 35.5 25.8 均值Mean/ (g·kg−1) 32.9 34.3 34.0 28.0 变异系数Coefficient 44.7 34.4 20.1 26.0 胡敏素
Humin范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 47 ~ 255 37 ~ 248 97 ~ 246 52 ~ 227 中值Median /(g·kg−1) 164 157 168 168 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 159 158 156 157 变异系数Coefficient 37.8 41.8 27.5 33.0 2.4 畜禽粪肥质量指标主成分分析及质量综合评价
主成分分析是利用降维思想,将多个指标转化为少数综合指标的统计方法[23]。首先将各指标数据通过隶属函数进行标准化,再将标准化后的14项指标的数据进行主成分分析,结果显示14项指标的KMO (Kaiser-Meyer-Olkin) 值为0.664(> 0.6),所选指标可进行主成分分析,得到相关矩阵的特征值、方差贡献率和主成分载荷矩阵。
前5个主成分特征值均大于1且累计贡献率达80.0%,包含了畜禽粪肥品质的大部分信息(表4)。第1主成分的贡献率为32.7%,主要由种子发芽指数、有机质的质量分数、可溶性有机质和胡敏素4个因子决定,表征了畜禽粪肥安全性及改土作用。第2主成分贡献率为18.4%,主要由腐殖酸、胡敏酸和富里酸3个因子决定,表征了畜禽粪肥提供活跃有机组分的能力。第3主成分贡献率为12.2%,主要由Hg决定。第4主成分贡献率为8.70%,主要由Pb决定,两个主成分表征了畜禽粪肥受重金属污染程度。第5主成分贡献率为8.11%,主要由总养分的质量分数决定,表征畜禽粪肥的供肥能力。
表 4 畜禽粪肥质量指标主成分分析Table 4 Principal component analysis of quality indexes of livestock and poultry manure指标
Index主成分 Principal component 1 2 3 4 5 种子发芽指数 Seed germination index 0.766 0.239 −0.446 −0.152 0.032 总养分的质量分数Total nutrient content −0.026 0.401 0.178 −0.276 0.771 有机质的质量分数 Organic matter content −0.841 0.120 0.234 0.046 −0.084 氯离子质量分数 Chloride ion content 0.382 0.387 0.179 0.571 0.360 As 0.683 −0.064 −0.111 0.221 −0.356 Cd 0.691 −0.107 0.061 0.095 0.349 Cr 0.578 −0.380 0.506 −0.370 −0.078 Hg 0.249 −0.427 0.805 −0.163 −0.035 Pb 0.380 −0.266 0.389 0.665 0.000 可溶性有机质 Dissolved organic matter 0.765 0.295 −0.211 −0.039 −0.067 腐殖酸 Humic acid 0.028 0.822 0.419 −0.088 −0.285 胡敏酸 Humilic acid 0.533 0.669 0.135 0.022 −0.231 富里酸 Fulvic acid −0.373 0.752 0.272 −0.025 −0.090 胡敏素 Humin −0.799 0 −0.060 0.343 0.009 特征值 Eigen value 4.571 2.571 1.705 1.218 1.135 贡献率 Contribution rate/% 32.7 18.4 12.2 8.70 8.11 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 32.7 51.0 63.2 71.9 80.0 根据标准化后的各指标与因子载荷矩阵计算各主成分的得分,公式如下:
$$ \begin{split} {\rm{F}}_{1}=&0.36{\rm{X}}_{1}-0.01{\rm{X}}_{2}-0.39{\rm{X}}_{3}+0.18{\rm{X}}_{4}+0.32{\rm{X}}_{5}+0.32{\rm{X}}_{6}+0.27{\rm{X}}_{7}+0.12{\rm{X}}_{8}+0.18{\rm{X}}_{9}+0.36{\rm{X}}_{10}+\\ &0.01{\rm{X}}_{11}+0.25{\rm{X}}_{12}-0.17{\rm{X}}_{13}-0.37{\rm{X}}_{14} \end{split} $$ (1) $$ \begin{split} {\rm{F}}_{2}=&0.15{\rm{X}}_{1}+0.25{\rm{X}}_{2}-0.07{\rm{X}}_{3}+0.24{\rm{X}}_{4}-0.04{\rm{X}}_{5}-0.07{\rm{X}}_{6}-0.24{\rm{X}}_{7}-0.27{\rm{X}}_{8}-0.17{\rm{X}}_{9}+0.18{\rm{X}}_{10}+\\ &0.51{\rm{X}}_{11}+0.42{\rm{X}}_{12}+0.47{\rm{X}}_{13}+0.00{\rm{X}}_{14 } \end{split} $$ (2) $$ \begin{split} {\rm{F}}_{3}=&-0.34{\rm{X}}_{1}+0.14{\rm{X}}_{2}+0.18{\rm{X}}_{3}+0.14{\rm{X}}_{4}-0.09{\rm{X}}_{5}+0.05{\rm{X}}_{6}+0.39{\rm{X}}_{7}+0.62{\rm{X}}_{8}+0.30{\rm{X}}_{9}-0.16{\rm{X}}_{10}+\\ &0.32{\rm{X}}_{11}+0.10{\rm{X}}_{12}-0.21{\rm{X}}_{13}-0.05{\rm{X}}_{14 } \end{split} $$ (3) $$ \begin{split} {\rm{F}}_{4}=&-0.14{\rm{X}}_{1}-0.25{\rm{X}}_{2}+0.04{\rm{X}}_{3}+0.52{\rm{X}}_{4}+0.20{\rm{X}}_{5}+0.09{\rm{X}}_{6}-0.34{\rm{X}}_{7}-0.15{\rm{X}}_{8}+0.60{\rm{X}}_{9}-0.04{\rm{X}}_{10}-\\ &0.08{\rm{X}}_{11}+0.02{\rm{X}}_{12}-0.02{\rm{X}}_{13}+0.31{\rm{X}}_{14 } \end{split} $$ (4) $$ \begin{split} {\rm{F}}_{5}=&0.03{\rm{X}}_{1}+0.72{\rm{X}}_{2}-0.08{\rm{X}}_{3}+0.34{\rm{X}}_{4}-0.33{\rm{X}}_{5}+0.33{\rm{X}}_{6}-0.07{\rm{X}}_{7}-0.03{\rm{X}}_{8}+0.00{\rm{X}}_{9}-0.06{\rm{X}}_{10}-\\ &0.27{\rm{X}}_{11}-0.22{\rm{X}}_{12}-0.08{\rm{X}}_{13}+0.01{\rm{X}}_{14} \end{split} $$ (5) 式中:X1、X2、X3、X4、X5、X6、X7、X8、X9、X10、X11、X12、X13、X14分别为种子发芽指数、总养分的质量分数、有机质的质量分数、氯离子质量分数、As、Cd、Cr、Hg、Pb、可溶性有机质、腐殖酸、胡敏酸、富里酸和胡敏素测定值经隶属函数标准化后的数据,F1、F2、F3、F4、F5分别为主成分1-5的得分值。
以每个主成分对应的贡献率所占提取主成分累计贡献率的比例为权重,主成分的得分与相应权重的乘积累加建立畜禽粪肥质量综合得分的数学模型:
$$ {\rm{F}}=0.41{\rm{F}}_{1}+0.23{\rm{F}}_{2}+0.15{\rm{F}}_{3}+0.11{\rm{F}}_{4}+0.10{\rm{F}}_{5 } $$ (6) 利用该模型计算各畜禽粪肥样品质量综合得分, 并根据不同畜禽粪肥样品平均综合得分进行优良度排序(表5)。牛粪肥的综合排名最高,在第一、二、四主成分中得分最高,在第三和第五主成分中得分排名第二,表明牛粪肥的安全性最高,改土作用最好,提供活跃有机组分的能力最强,肥料重金属含量低。羊粪肥综合排名第二,各主成分排名均低于牛粪肥,各方面指标评分均低于牛粪肥。猪粪肥综合排名第三,但其第三、第五主成分得分最高,表明猪粪肥受重金属污染程度低,且供肥能力在4种畜禽粪肥中最强。鸡粪肥综合排名第四,但其第二主成分排名高于猪粪肥和羊粪肥,表明其提供活跃有机组分的能力要优于这两种畜禽粪肥。
表 5 不同畜禽粪肥各主成分平均得分及总得分表Table 5 Average score and total score of main components of different livestock and poultry manure种类
Type1 2 3 4 5 综合评价
Comprehensive evaluation得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort猪粪肥Pig manure 0.94 3 0.42 4 1.28 1 0.5 2 0.043 1 0.73 3 牛粪肥Cattle manure 1.12 1 0.53 1 1.28 2 0.56 1 0.017 2 0.83 1 羊粪肥Sheep manure 1.01 2 0.46 3 1.26 3 0.46 3 −0.01 3 0.76 2 鸡粪肥Chicken manure 0.68 4 0.49 2 0.84 4 0.02 4 −0.12 4 0.51 4 3 结 论
黑龙江省松嫩平原黑土区自然堆置的粪肥腐熟度普遍低于行业标准。4种畜禽粪肥中,牛粪肥的质量最好,其腐熟度最高,提供活跃有机组分的能力最强,重金属含量最低。其次是羊粪肥,其各方面指标评分均低于牛粪肥。再次是猪粪肥,其氮磷钾养分含量虽高于其他粪肥,但腐熟度偏低,水分含量偏高,提供活跃有机组分的能力较弱。鸡粪肥各方面指标均不如其它粪肥,重金属超标率相对较高。黑龙江省松嫩平原黑土区自然堆置的畜禽粪肥需要进一步腐熟以提高其安全性,牛粪是最佳的有机肥物料来源。
-
表 1 不同畜禽粪肥的技术指标
Table 1 Technical indexes of different livestock and poultry manure
技术指标
Technical index猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manure有机质的质量分数
Organic matter content范围Range/% 21.5 ~ 86.5 24.1 ~ 82.1 31.4 ~ 78.2 27.9 ~ 60.4 中值Median/% 46.9 44.6 45.6 39.9 均值Mean/% 48.5 45.4 48.1 40.4 变异系数Coefficient 42.3 32.0 25.0 23.9 标准Criteria/% ≥30 ≥30 ≥30 ≥30 达标率Compliance rate/% 81 89 100 89 总养分的质量分数
Total nutrient content范围Range/% 3.14 ~ 8.86 2.65 ~ 7.97 2.84 ~ 5.71 2.25 ~ 4.87 中值Median/% 5.00 4.06 4.26 3.87 均值Mean/% 5.39 4.29 4.39 3.83 变异系数Coefficient 35.2 29.7 18.8 21.1 标准Criteria/% ≥4 ≥4 ≥4 ≥4 达标率Compliance rate/% 75 57 71 44 酸碱度
pH范围Range 5.9 ~ 8.7 6.4 ~ 8.6 6.0 ~ 9.4 7.0 ~ 9.0 中值Median 7.8 7.8 8.1 8.3 均值Mean 7.5 7.7 8.0 8.0 变异系数Coefficient 13.1 6.7 12.3 8.1 标准Criteria 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 5.5 ~ 8.5 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 96 71 78 水分的质量分数
Moisture content范围Range/% 15.7 ~ 68.0 15.0 ~ 59.0 17.8 ~ 60.6 17.5 ~ 37.0 中值Median/% 43.0 28.2 29.5 28.0 均值Mean/% 39.5 31.7 33.6 28.4 变异系数Coefficient 38.9 42.0 39.4 19.7 标准Criteria/% ≤30 ≤30 ≤30 ≤30 达标率Compliance rate/% 38 64 50 67 机械杂质质量分数
Mechanical impurity content范围Range/% 0 ~ 0.99 0 ~ 0.97 0 ~ 0.96 0.52 ~ 0.97 中值Median/% 0.61 0.43 0.41 0.86 均值Mean/% 0.53 0.42 0.44 0.80 变异系数Coefficient 67.4 85.7 87.0 43.3 标准Criteria/% ≤0.5 ≤0.5 ≤0.5 ≤0.5 达标率Compliance rate/% 38 57 57 0 注:各指标标准参考有机肥农业行业标准(NY/T525-2021)[8]。 Note: The index standards refer to the Agricultural Industry Standard of Organic Fertilizer (NY/T525-2021)[8]. 表 2 不同畜禽粪肥的限量指标
Table 2 Limit indexes of different livestock and poultry manure
限量指标
Limit index猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manureAs 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.95 ~ 15.1 1.55 ~ 19.7 1.68 ~ 20.0 7.59 ~ 16.8 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 4.45 6.50 7.43 9.53 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 5.96 7.71 8.08 12.1 变异系数Coefficient 81.6 69.5 67.0 33.1 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤15 ≤15 ≤15 ≤15 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 86 86 56 Cd 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.74 ~ 3.45 0.28 ~ 2.16 0.28 ~ 3.07 1.07 ~ 3.22 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 1.51 1.34 1.24 1.91 均值Mean(/mg·kg−1) 1.68 1.24 1.44 2.04 变异系数Coefficient 48.9 44.0 52.1 34.4 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤3 ≤3 ≤3 ≤3 达标率Compliance rate/% 88 100 93 78 Cr 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 3.2 ~ 61.4 0.3 ~ 47.9 5.6 ~ 31.0 7.2 ~ 69.1 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 17.1 12.5 11.9 21.8 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 20.0 17.5 15.4 28.0 变异系数Coefficient 70.5 69.1 53.9 84.5 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤150 ≤150 ≤150 ≤150 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 100 Hg 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.08 ~ 0.31 0.05 ~ 0.34 0.04 ~ 0.41 0.07 ~ 1.71 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 0.16 0.12 0.13 0.16 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 0.17 0.13 0.17 0.48 变异系数Coefficient 34.5 52.4 70.4 141.7 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤2 ≤2 ≤2 ≤2 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 100 Pb 范围Range/(mg·kg−1) 0.66 ~ 34.2 1.51 ~ 29.7 1.03 ~ 39.6 33.5 ~ 56.3 中值Median/(mg·kg−1) 6.70 10.23 8.53 51.41 均值Mean/(mg·kg−1) 9.71 11.85 14.0 47.9 变异系数Coefficient 107.1 69.6 98.0 17.8 标准Criteria/(mg·kg−1) ≤50 ≤50 ≤50 ≤50 达标率Compliance rate/% 100 100 100 33 氯离子质量分数
Chloride ion content范围Range/% 0.31 ~ 1.99 0.16 ~ 1.99 0.21 ~ 1.91 1.23 ~ 1.96 中值Median/% 1.15 0.70 1.00 1.69 均值Mean/% 1.20 0.87 1.10 1.60 变异系数Coefficient 47.3 66.5 39.1 18.9 杂草种子活性
Weed seed activity范围Range/(株·kg−1) 0 0 ~ 2 0 ~ 5 0 中值Median/(株·kg−1) 0 1 2 0 均值Mean/(株·kg−1) 0 0.71 2.07 0 变异系数Coefficient 0.0 92.2 83.5 0.0 注:各指标标准参考有机肥农业行业标准(NY/T525-2021)[8]。 Note: The index standards refer to the Agricultural Industry Standard of Organic Fertilizer (NY/T525-2021) [8]. 表 3 不同畜禽粪肥的有机组分
Table 3 Organic components of different livestock and poultry manure
有机组分
Organic component猪粪肥
Pig manure牛粪肥
Cattle manure羊粪肥
Sheep manure鸡粪肥
Chicken manure可溶性有机质
Dissolved organic matter范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 1.1 ~ 24.9 5.9 ~ 24.8 5.4 ~ 22.2 4.3 ~ 24.2 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 11.7 14.3 14.0 12.5 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 11.8 14.3 13.8 13.1 变异系数Coefficient 62.0 34.4 37.0 48.2 腐殖酸
Extractable humic acid
范围Range /(g·kg−1) 25.4 ~ 97.4 21.1 ~ 97.4 36.1 ~ 72.6 31.6 ~ 67.5 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 61.1 65.4 60.3 61.4 均值Mean/ (g·kg−1) 56.9 64.8 59.2 55.3 变异系数Coefficient 36.0 29.4 17.7 22.4 胡敏酸
Humic acid
范围Range /(g·kg−1) 8.7 ~ 40.3 6.7 ~ 46.0 7.4 ~ 45.4 14.0 ~ 39.3 中值Median/ (g·kg−1) 22.8 27.5 23.5 29.0 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 23.9 27.5 25.1 27.3 变异系数Coefficient 44.1 34.3 46.1 29.0 富里酸
Fulvic acid范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 11.4 ~ 60.4 11.0 ~ 52.5 12.7 ~ 40.0 17.5 ~ 42.3 中值Median /(g·kg−1) 31.3 35.3 35.5 25.8 均值Mean/ (g·kg−1) 32.9 34.3 34.0 28.0 变异系数Coefficient 44.7 34.4 20.1 26.0 胡敏素
Humin范围Range/ (g·kg−1) 47 ~ 255 37 ~ 248 97 ~ 246 52 ~ 227 中值Median /(g·kg−1) 164 157 168 168 均值Mean /(g·kg−1) 159 158 156 157 变异系数Coefficient 37.8 41.8 27.5 33.0 表 4 畜禽粪肥质量指标主成分分析
Table 4 Principal component analysis of quality indexes of livestock and poultry manure
指标
Index主成分 Principal component 1 2 3 4 5 种子发芽指数 Seed germination index 0.766 0.239 −0.446 −0.152 0.032 总养分的质量分数Total nutrient content −0.026 0.401 0.178 −0.276 0.771 有机质的质量分数 Organic matter content −0.841 0.120 0.234 0.046 −0.084 氯离子质量分数 Chloride ion content 0.382 0.387 0.179 0.571 0.360 As 0.683 −0.064 −0.111 0.221 −0.356 Cd 0.691 −0.107 0.061 0.095 0.349 Cr 0.578 −0.380 0.506 −0.370 −0.078 Hg 0.249 −0.427 0.805 −0.163 −0.035 Pb 0.380 −0.266 0.389 0.665 0.000 可溶性有机质 Dissolved organic matter 0.765 0.295 −0.211 −0.039 −0.067 腐殖酸 Humic acid 0.028 0.822 0.419 −0.088 −0.285 胡敏酸 Humilic acid 0.533 0.669 0.135 0.022 −0.231 富里酸 Fulvic acid −0.373 0.752 0.272 −0.025 −0.090 胡敏素 Humin −0.799 0 −0.060 0.343 0.009 特征值 Eigen value 4.571 2.571 1.705 1.218 1.135 贡献率 Contribution rate/% 32.7 18.4 12.2 8.70 8.11 累计贡献率 Cumulative contribution rate/% 32.7 51.0 63.2 71.9 80.0 表 5 不同畜禽粪肥各主成分平均得分及总得分表
Table 5 Average score and total score of main components of different livestock and poultry manure
种类
Type1 2 3 4 5 综合评价
Comprehensive evaluation得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort得分
Score排序
Sort猪粪肥Pig manure 0.94 3 0.42 4 1.28 1 0.5 2 0.043 1 0.73 3 牛粪肥Cattle manure 1.12 1 0.53 1 1.28 2 0.56 1 0.017 2 0.83 1 羊粪肥Sheep manure 1.01 2 0.46 3 1.26 3 0.46 3 −0.01 3 0.76 2 鸡粪肥Chicken manure 0.68 4 0.49 2 0.84 4 0.02 4 −0.12 4 0.51 4 -
[1] 刘洪彬,李顺婷,吴梦瑶,等. 耕地数量、质量、生态“三位一体”视角下我国东北黑土地保护现状及其实现路径选择研究[J]. 土壤通报,2021,52(3):544−552. LIU H B,LI S T,WU M Y,et al. Current situation and perspectives of black soil protection from the integrated angle of quantity, quality, and ecology in northeast China[J]. Chinese Journal of Soil Science,2021,52 (3):544−552.
[2] 魏丹,匡恩俊,迟凤琴,等. 东北黑土资源现状与保护策略[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2016(1):158−161. WEI D,KUANG E J,CHI F Q,et al. Status and protection strategy of black soil resources in northeast of China[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2016 (1):158−161.
[3] 武红亮,王士超,槐圣昌,等. 近30年来典型黑土肥力和生产力演变特征[J]. 植物营养与肥料学报,2018,24(6):1456−1464. WU H L,WANG S C,HUAI S C,et al. Evolutionary characteristics of fertility and productivity of typical black soil in recent 30 years[J]. Journal of Plant Nutrition and Fertilizers,2018,24 (6):1456−1464.
[4] 魏玉杰,田俊影,蔡崇法. 我国东北地区有机肥资源分布特征与养分利用潜力分析[J]. 农业资源与环境学报,2023,40(4):745−754. WEI Y J,TIAN J Y,CAI C F. Spatial distribution and nutrient utilization potential of organic fertilizer resources in the black soil region of northeast China[J]. Journal of Agricultural Resources and Environment,2023,40 (4):745−754.
[5] 聂文军,嘎毕拉,金忠民,等. 对比研究槽式堆肥处理不同畜禽粪便对植物毒性的影响[J]. 环境科学学报,2020,40(7):2557−2570. NIE W J,GA B L,JIN Z M,et al. Comparison of changes of different animal-manures composted by trough composting process and their effects on phytotoxicities[J]. Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2020,40 (7):2557−2570.
[6] 李文圣,王旭东. 猪粪和牛粪与秸秆配合堆腐过程中腐殖物质的变化特征[J]. 生态与农村环境学报,2014,30(4):541−544. LI W S,WANG X D. Variation of humus in mixture of swine or bovine manure and wheat straw during composting[J]. Journal of Ecology and Rural Environment,2014,30 (4):541−544.
[7] DING X L,YUAN Y R,LIANG Y,et al. Impact of long-term application of manure, crop residue, and mineral fertilizer on organic carbon pools and crop yields in a Mollisol[J]. Journal of Soils and Sediments,2014,14 (5):854−859. DOI: 10.1007/s11368-013-0840-x
[8] 中华人民共和国农业农村部. 有机肥料: NY/T525-2021[S]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China. Organic fertilizer: NY/T525-2021[S]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2021.
[9] ZHOU Y,SELVAM A,WONG J W C. Evaluation of humic substances during co-composting of food waste, sawdust and Chinese medicinal herbal residues[J]. Bioresource Technology,2014,168:229−234. DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2014.05.070
[10] 鲍士旦. 土壤农化分析 [M]. 3版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2000. BAO S D. Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis [M]. 3rd ed. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2000.
[11] 王国英,袁京,孔艺霖,等. 堆肥种子发芽指数测定方法与敏感性种子筛选[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(19):220−227. WANG G Y,YUAN J,KONG Y L,et al. Determination of seed germination index and selection of sensitive seeds for phytotoxicity evaluation of composting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37 (19):220−227.
[12] 李洋,席北斗,赵越,等. 不同物料堆肥腐熟度评价指标的变化特性[J]. 环境科学研究,2014,27(6):623−627. LI Y,XI B D,ZHAO Y,et al. Study of maturity parameter characteristics in composting process using different materials[J]. Research of Environmental Sciences,2014,27 (6):623−627.
[13] 黄光群,黄晶,张阳,等. 沼渣好氧堆肥种子发芽指数快速预测可行性分析[J]. 农业机械学报,2016,47(5):177−182. HUANG G Q,HUANG J,ZHANG Y,et al. Feasibility analysis of rapid prediction of seed germination index during digestate aerobic composting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2016,47 (5):177−182.
[14] 刘凯,郁继华,颉建明,等. 不同配比的牛粪与玉米秸秆对高温堆肥的影响[J]. 甘肃农业大学学报,2011,46(1):82−88. LIU K,YU J H,XIE J M,et al. Effects of different ratios of dairy manure and corn stalk on high temperature composting process[J]. Journal of Gansu Agricultural University,2011,46 (1):82−88.
[15] 魏宗强,罗一鸣,吴绍华,等. 添加沸石对鸡粪高温堆肥磷钾径流及淋洗损失的影响[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2012,31(12):2486−2492. WEI Z Q,LUO Y M,WU S H,et al. Effects of zeolite addition on the loss of phosphorus and potassium through runoff and leaching in poultry manure composting[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2012,31 (12):2486−2492.
[16] LU K P,YANG X,SHEN J J,et al. Effect of bamboo and rice straw biochars on the bioavailability of Cd, Cu, Pb and Zn to Sedum plumbizincicola[J]. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment,2014,191:124−132.
[17] XU D Y,ZHAO Y,SUN K,et al. Cadmium adsorption on plant- and manure-derived biochar and biochar-amended sandy soils: impact of bulk and surface properties[J]. Chemosphere,2014,111:320−326. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.04.043
[18] 王广耀,李雪,周昶延,等. 滑子菇渣与猪粪不同配比对堆肥腐殖质组成的影响[J]. 华南农业大学学报,2019,40(6):111−117. WANG G Y,LI X,ZHOU C Y,et al. Effects of different ratios of Pholiota nameko residue to pig manure on compost humus composition[J]. Journal of South China Agricultural University,2019,40 (6):111−117.
[19] 李恕艳,李吉进,张邦喜,等. 菌剂对鸡粪堆肥腐殖质含量品质的影响[J]. 农业工程学报,2016,32(S2):268−274. LI S Y,LI J J,ZHANG B X,et al. Influence of inoculants on content and quality of humus during chicken manure composting[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2016,32 (S2):268−274.
[20] SHAN Y,CHEN J H,WANG L,et al. Influences of adding easily degradable organic waste on the minimization and humification of organic matter during straw composting[J]. Journal of Environmental Science and Health Part B, Pesticides, Food Contaminants, and Agricultural Wastes,2013,48 (5):384−392.
[21] 王玉军,窦森,张晋京,等. 农业废弃物堆肥过程中腐殖质组成变化[J]. 东北林业大学学报,2009,37(8):79−81. WANG Y J,DOU S,ZHANG J J,et al. Changes of humic components during agricultural waste composting[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University,2009,37 (8):79−81.
[22] 窦森,于水强,张晋京. 不同CO2浓度对玉米秸秆分解期间土壤腐殖质形成的影响[J]. 土壤学报,2007,44(3):458−466. DOU S,YU S Q,ZHANG J J. Effects of carbon dioxide concentration on humus formation in corn stalk decomposition[J]. Acta Pedologica Sinica,2007,44 (3):458−466.
[23] 乌凤章,张润梅,尹泽宇,等. 基于主成分分析的高丛蓝莓品种果实品质综合评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(22):262−269. WU F Z,ZHANG R M,YIN Z Y,et al. Comprehensive quality evaluation of highbush blueberry cultivars based on principal component analysis[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38 (22):262−269.



 下载:
下载: